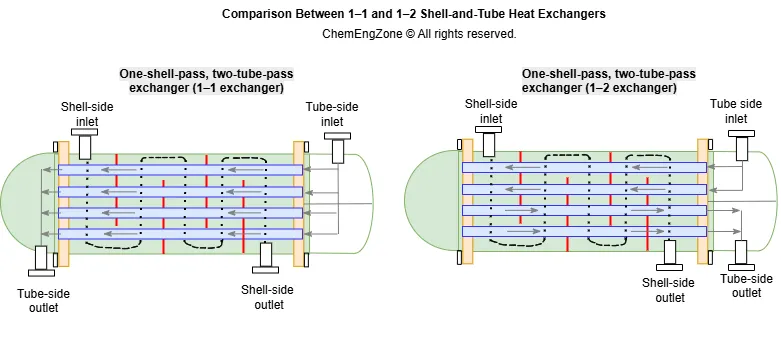
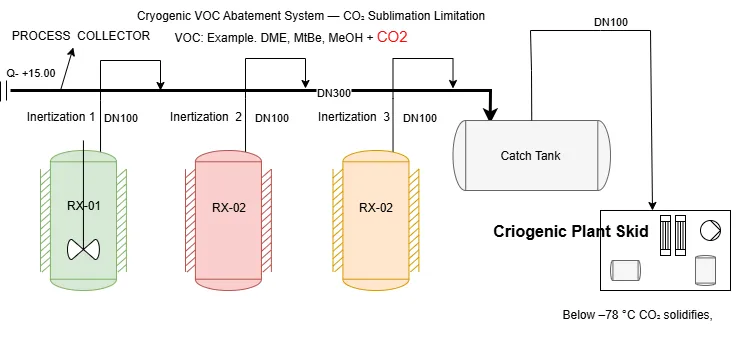
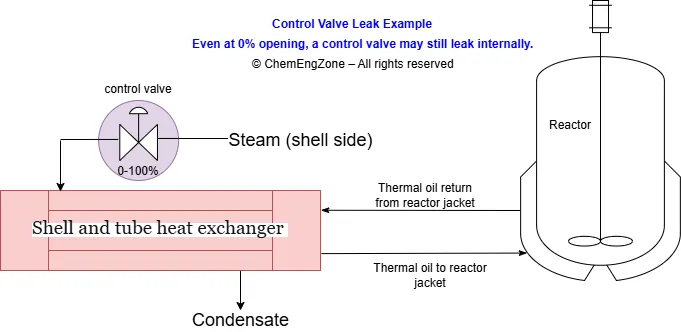
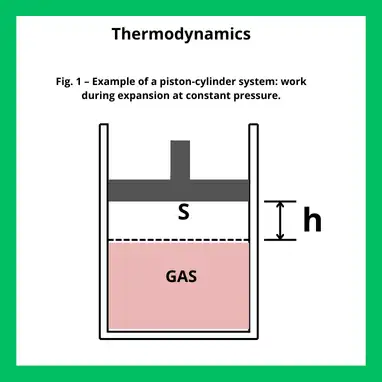
Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design
A shell and tube heat exchanger transfers heat between two separated fluids using a tube bundle inside a cylindrical shell. This article explains its construction, flow arrangements (1–1 and 1–2), and key design principles used in chemical engineering.