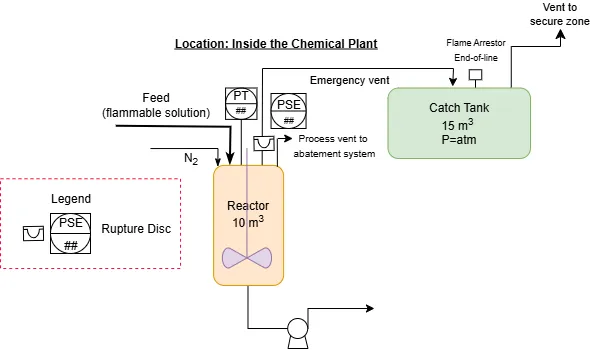
LOPA & SIL: Practical Examples
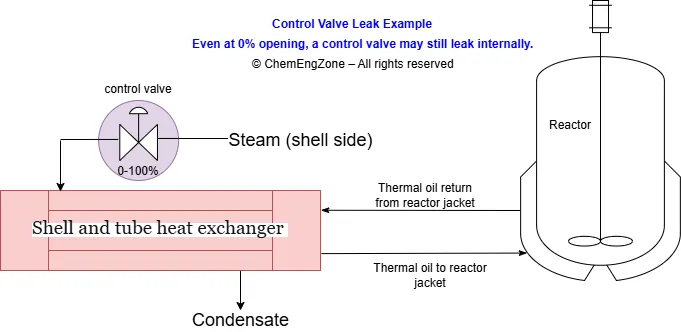
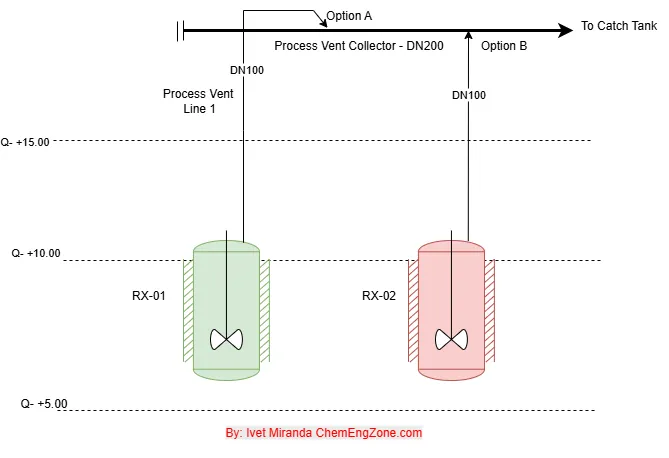
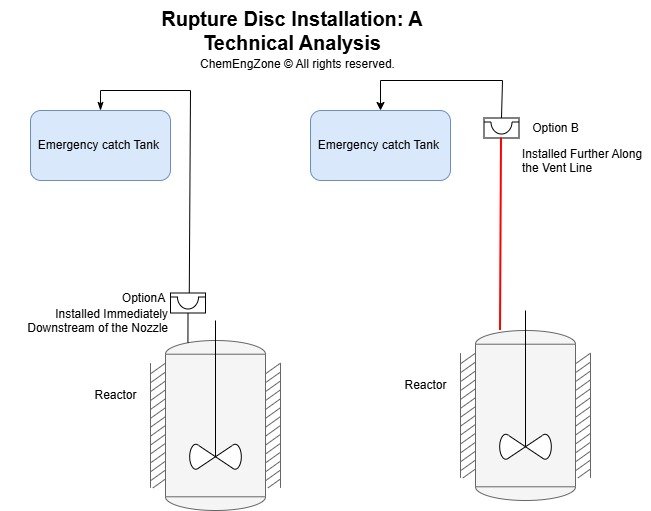
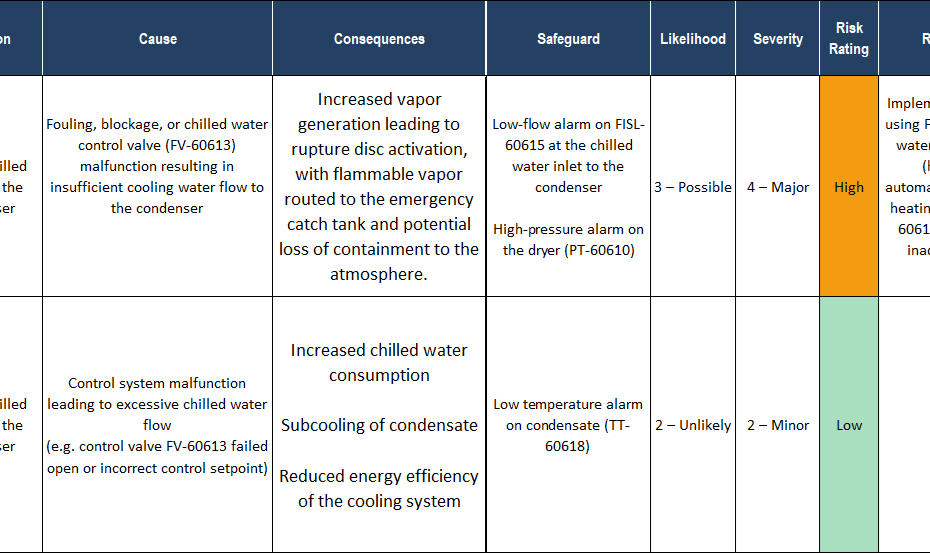
A LOPA analysis is required only when the residual frequency of a major accident scenario remains too high after all independent protection layers are considered. This article explains how HAZOP identifies the hazardous scenarios, how LOPA quantifies the risk gap, and when a SIL-rated safety function becomes necessary—illustrated through two practical process examples.